

For Northern Ireland see Technical Booklet N for guidance.Ī percolation test determines the rate of infiltration into the ground by measuring how long it takes water to drop in a saturated hole dug in soil therefore, determining the suitability of the soil. Seek advice for SEPA's guidelines for indirect sewage discharges to groundwater, regulatory method WAT-RM-04, and building standards guidance from the Scottish Government.
Septic tank and drain field layout code#
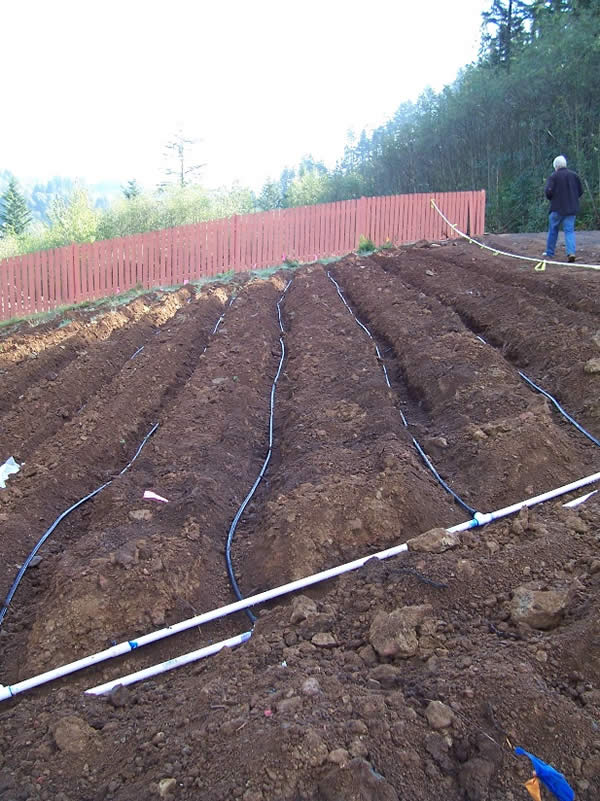
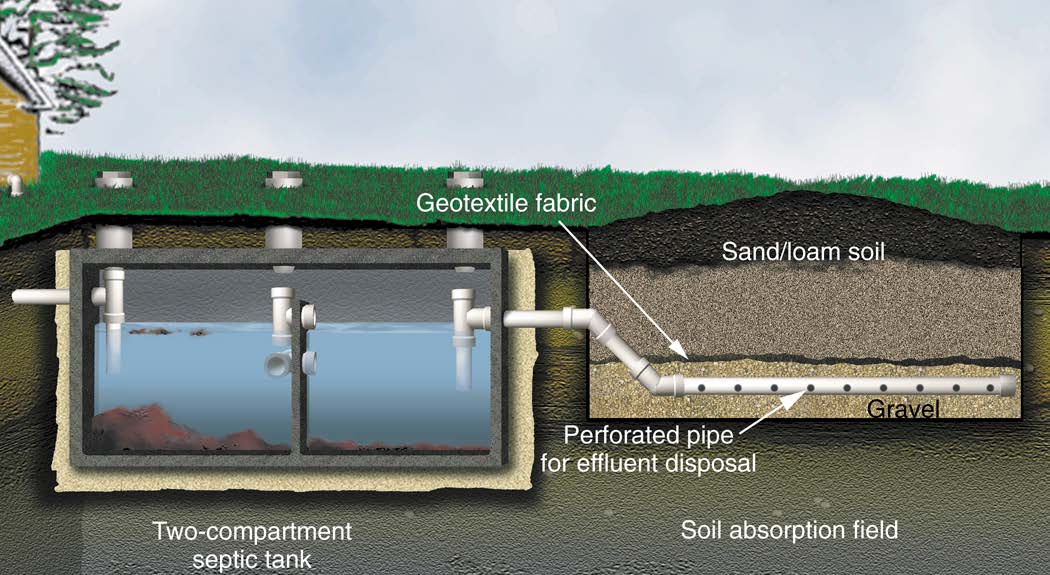
The guidelines for the design of drainage fields can be found in Building Regulations Part H for England, which also applies to building work carried out on excepted energy buildings in Wales.įor Scotland and Northern Ireland drainage fields should conform to BS 6297, the code of practice for the design and installation of drainage fields for use in wastewater treatment. The septic tank only performs around 45% of the treatment work, the rest of the work is performed by the drain field which is why it is so important to make sure it is designed correctly prior to installation. It usually consists of an arrangement of trenches, which contain perforated pipes and gravel, sited beneath a soft landscaped area such as a lawn.Īs well as the septic tank, the septic drain field and any other connecting pipework make up the septic system. Learn more about leach field issues and maintenance here.Septic drainage fields, sometimes referred to as septic drain fields, leach fields or foul water soakaways, are subsurface wastewater treatment facilities which are used to remove contaminants and impurities from the effluent that emerges from a septic tank.
Septic tank and drain field layout professional#
For this reason, having your professional plumber come out to first properly diagnose the problem is so important. Some signs of a failed box could look very similar to a septic tank system blockage or a leach field issue. However, in the event of sludge buildup, tree root invasions, improper maintenance, heavy machinery on top of the box or other issues that can cause unrepairable damage to your distribution box, you may need to replace it. By being proactive, you can make minor adjustments or repairs as needed to hopefully prevent unnecessary large issues, failures, or backups.Ī concrete D-box can typically last up to 20 years.
Inspections help to ensure that your system is working properly before major issues occur or warning signs are presented. Interior – The interior of your distribution box can indicate some issues with your system (past or present), like flood lines.Uneven Distribution – If a D-box has tilted or tipped, this could result in distribution to only one section of leach fields, which could result in overflow of effluent to the surface, or a system backup or clog.Outlets & Openings – Most well-designed systems will allow for the outlet openings to be adjusted to regulate the flow if necessary.Some important inspection points of your distribution box are: While a D-box does not need to be pumped regularly like your septic tank, it should be inspected to make sure it is in proper working condition. You can also look for a depression in the ground between the septic tank and drain field a couple of feet in diameter.If your layout consists of a rectangular and level drain site, it’s likely that your distribution box will be located near the edge of the drain field, closest to the septic tank.The location of the distribution box depends mostly on space and layout of the septic’s drain field.

How Do I Find My Septic Tank Distribution Box? They are most commonly constructed out of concrete or plastic with a design that encompasses several holes to allow for easy flow out into the leach fields. The size and shape of your septic tank’s distribution box is dependent on the size of your septic system itself. Once the wastewater flows out of the septic tank, it moves to the distributor box and then out into the leach fields. To put it simply, its job is to evenly distribute the wastewater into the leach field. A septic tank’s distribution box (or a D-box) is a container that receives the septic tank effluent and re-distributes it into the network of attached drain fields and pipes. One of these parts that is often forgot about, or homeowners simply don’t know exists is the distribution box. Since septic tanks are buried underground, it’s easy to not really understand all of the moving parts within the system.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
